The Future is Now: How AI is Revolutionizing Manufacturing Industry
Risk Trends
Oct 11, 2024

Jowanza Joseph
CEO, Parakeet Risk

From improving efficiency and safety to enhancing product development and supply chain management, AI is a game-changer for manufacturers of all sizes. Explore the main takeaways from the NAM whitepaper, examining how AI is being implemented, its benefits, and the challenges ahead.
Key Highlights
Whether you're a manufacturing professional, a policymaker, or simply someone interested in the intersection of AI and industry, this exploration of the NAM whitepaper will provide valuable insights into one of the most significant technological shifts of our time.
We’ll also look at the policy recommendations put forward by NAM to ensure that the U.S. remains a global leader in AI-driven manufacturing innovation. Alongside AI, emerging technologies such as digital twins and edge computing are also driving efficiency, sustainability, and operational resilience.
NAM's insights on AI in the Manufacturing Industry in a Nutshell
In May 2024, the National Association of Manufacturers (NAM) released a whitepaper titled “Working Smarter: How Manufacturers Are Using Artificial Intelligence.” This report offers a fascinating glimpse into AI’s current state and future potential in the manufacturing sector. AI's impact on the manufacturing industry is already being felt, shaping both present operations and the future direction of industrial innovation. As we delve into the key findings, it becomes clear that we’re not just discussing a future possibility - AI is already transforming manufacturing profoundly.
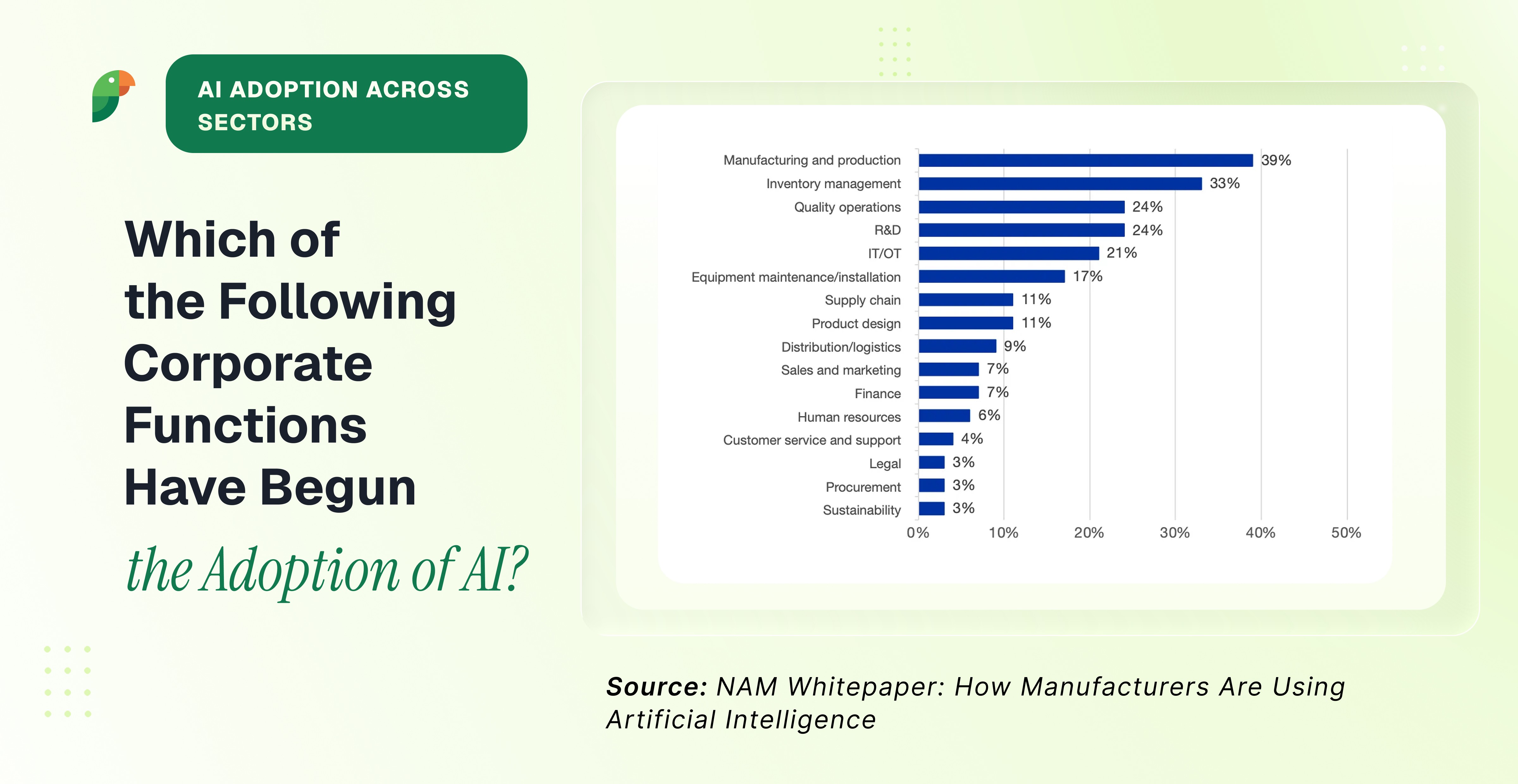
The State of AI Adoption in Manufacturing
The NAM whitepaper reveals that AI adoption in manufacturing is not a future trend - it’s happening rapidly. As of October 2023, 74% of surveyed manufacturers had already invested in machine learning or planned to do so. This statistic alone speaks volumes about the industry’s recognition of AI’s potential.
What’s particularly interesting is the dual role that manufacturers are playing in the AI landscape. They’re not just consumers of AI technologies developed by tech companies; many are actively developing AI tools tailored to their needs. This trend towards in-house AI development showcases the manufacturing sector’s innovative spirit and determination to harness AI’s full potential.
The whitepaper identifies several key areas where AI is making significant inroads:
Manufacturing and production
Inventory management
Quality operations and R&D
Predictive maintenance
Supply chain management
Product development and design
Safety improvements
Worker training and knowledge management
AI algorithms and machine learning models are widely used for process optimization and predictive analytics in manufacturing. They analyze sensor data to predict equipment failures, improve quality control, and enhance efficiency.
Generative AI enables design engineers to input requirements and generate multiple optimized iterations that can be more innovative than traditional methods. It streamlines development across industries such as aerospace and automotive.
This adaptability highlights AI's role in overcoming manufacturing challenges, with deep learning enabling advanced pattern recognition and self-improvement. Notably, AI adoption is growing among manufacturers of all sizes, showcasing its democratization. AI is transforming production methods through simulation, optimization, and custom product creation, enabling even smaller manufacturers to remain competitive in a tech-driven market.
AI applications deliver remarkable results across the entire value stream in manufacturing.
AI Technologies and Applications for Industries
AI technologies are rapidly transforming the manufacturing industry, delivering unprecedented efficiency and intelligence across production lines and supply chains. By integrating artificial intelligence into manufacturing processes, companies can harness machine learning and generative AI to streamline operations and drive innovation.
For example, AI models can analyze vast amounts of production data in real time, identify inefficiencies, and suggest process improvements that reduce operational costs and boost productivity.
On the factory floor, artificial intelligence provides real-time insights and decision support, enabling manufacturers to respond quickly to changing conditions. AI-powered systems can optimize energy consumption, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and waste is minimized.
In quality control, machine learning algorithms can detect defects and anomalies with greater accuracy than traditional methods, leading to higher product quality and fewer recalls.
Predictive maintenance is another key application in which AI models analyze sensor data to anticipate equipment failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. In supply chain optimization, AI helps manufacturers manage inventory levels, forecast demand, and identify alternative suppliers, making the entire supply chain more resilient and responsive. By leveraging these advanced technologies, manufacturers are not only reducing operational costs but also enhancing their overall operational efficiency and competitiveness in the global market.
Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
Digital transformation is reshaping the manufacturing industry by integrating advanced digital technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) into every aspect of production. This shift enables manufacturers to create highly connected and agile production environments, where data flows seamlessly between machines, systems, and people.
One of the most impactful innovations is the use of digital twins—virtual replicas of physical assets or processes. These digital twins allow manufacturers to simulate and optimize production schedules, test new designs, and troubleshoot issues without the need for costly physical prototypes. This not only accelerates product development but also enhances product quality assurance by identifying potential problems early in the process.
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is another area where digital transformation is making a significant difference. By enabling the rapid production of complex parts with minimal waste, additive manufacturing supports greater customization and faster time-to-market. The adoption of these digital technologies helps manufacturers remain competitive, improve operational efficiency, and adapt quickly to changing market demands. Ultimately, digital transformation empowers manufacturers to deliver higher-quality products, optimize production schedules, and maintain a leading edge in an increasingly digital world.
The Benefits of AI in Manufacturing
The NAM whitepaper presents a compelling case for the many benefits AI is delivering to the manufacturing sector. At the forefront are improved efficiency and cost reduction, with boosted productivity emerging as a key benefit. AI-powered systems are helping manufacturers optimize operations, reduce waste, and make more informed decisions.
For example, a chemical company uses machine learning to analyze reactor data for more informed process changes.
Other significant benefits include enhanced operational visibility and process optimization. AI tools provide manufacturers with unprecedented insights into their operations, enabling them to identify bottlenecks, predict maintenance needs, and optimize resource allocation. AI-driven systems also improve resource efficiency by optimizing resource allocation and utilization throughout production. This visibility level transforms how manufacturers approach everything from inventory management to equipment maintenance.
Quality control is another area where AI is making a significant impact. Machine vision systems, which 80% of surveyed manufacturers had invested in or planned to invest in, are used to detect defects that are difficult for the human eye to spot. In addition, AI can monitor production parameters in real time—such as temperature, humidity, and machine vibration—to improve product quality, increase yield, and reduce costs. This improves product quality, reduces waste, and enhances customer satisfaction.
Safety improvements are a crucial benefit of AI in manufacturing. The whitepaper mentions an automotive manufacturer using AI and machine vision to monitor intersections of production lanes and alert workers to potential hazards. AI-powered robots are also taking over repetitive processes and dangerous tasks, improving both safety and operational efficiency. Such applications prevent accidents and create a more comfortable and secure working environment.
AI is accelerating innovation in product development and design. The report cites a pharmaceutical company using AI models to identify new approaches to developing molecules and advancing individualized treatments for diseases. This application of AI has the potential to revolutionize not just manufacturing processes but also entire industries and research fields.
Supply chain resilience is another area where AI is proving invaluable. By analyzing large volumes of data, AI models can predict disruptions, optimize inventory levels, and recommend alternative suppliers or routes when issues arise. This capability is particularly crucial in an era of global supply chain challenges.
AI also plays a vital role in helping manufacturers reduce energy usage, minimize waste, and improve resource allocation, all of which contribute to cost reduction and sustainability. AI can track patterns in energy consumption and suggest improvements that reduce waste and lower costs. By streamlining operations, reducing manual tasks, and improving scheduling, AI applications lead to a more agile and productive workforce.
Lastly, the whitepaper highlights how AI is used for knowledge retention and transfer. As the manufacturing workforce ages, AI systems capture the knowledge of experienced workers and train new employees, ensuring that valuable expertise is preserved.
The Human-Centric Approach to AI in Manufacturing
One of the most reassuring aspects of the NAM whitepaper is its emphasis on a human-centric approach to AI implementation. Contrary to fears of widespread job displacement, manufacturers view AI as a tool to augment human capabilities rather than replace workers. AI-powered collaborative robots (cobots) are increasingly working alongside human operators, learning from them and adapting to tasks, which enhances both safety and flexibility on the shop floor.
The report stresses that manufacturers want to keep people’s work, not computers’, at the center of their operations. AI is seen as a “co-pilot” that enhances worker efficiency while still prioritizing human experience and ingenuity. AI assists human workers by providing real-time data and supporting decision-making, creating a partnership that improves output and increases workers’ trust and confidence in AI systems.
To support this human-centric approach, manufacturers invest heavily in workforce upskilling. Many companies are establishing training programs to help employees build confidence and competence with AI systems. Collaborative robots require minimal programming, making it easier for workers to adapt to new technologies. These programs often focus on safety and control, addressing potential risks and protecting intellectual property. AI-powered robots are also taking over dangerous tasks, improving workplace safety and operational efficiency.
Interestingly, AI is also changing recruitment practices. The whitepaper notes that some companies are increasing their hiring of data scientists to build and implement AI systems. This trend suggests that AI is not just changing existing jobs but also creating new roles and career paths within manufacturing.
The human-centric approach extends to knowledge management as well.
As of 2019, nearly a quarter of the manufacturing workforce was over 55.
Companies are using AI systems to capture and transfer the knowledge of experienced workers to new employees. This application of AI ensures that valuable expertise is retained even as the workforce evolves.
Looking ahead, AI will enhance human decision-making through advanced analytics, providing workers with real-time data and insights to make better decisions on the shop floor.
Implementation and Integration of AI for Manufacturing
Successfully integrating AI into manufacturing processes requires a strategic approach. Manufacturers begin by pinpointing areas where AI can deliver the most value, such as predictive maintenance, quality control, or supply chain optimization. Once these opportunities are identified, companies develop a roadmap for integrating AI, which may involve collaborating with technology partners or investing in new AI-powered tools.
Machine learning algorithms and generative AI are deployed to analyze production data, uncovering patterns and insights that drive continuous improvement. However, technology alone is not enough—skilled workers are essential to interpret AI-generated insights and implement changes on the shop floor. Training and upskilling employees ensures that human expertise complements AI capabilities, leading to better decision-making and smoother operations.
A phased adoption approach minimizes disruption, allowing for testing and refinement of AI solutions before wider implementation. By planning integration carefully and investing in technology and talent, manufacturers can enhance operational efficiency and optimize their supply chains.
Testing and Governance of AI Systems
The NAM whitepaper reveals that manufacturers are taking a proactive approach to ensuring the safety and reliability of AI systems. Many companies apply the same robust risk-management frameworks they use for IT and cybersecurity to their AI programs.
Testing groups that bring together AI, IT, and operations professionals are being formed to identify algorithm inaccuracies and validate that systems meet high success thresholds.
The report mentions a shipping and logistics company that found both internal facility safety teams and third-party testing organizations needed to develop new knowledge bases and upskill together to effectively test new AI systems.
Governance is another crucial aspect highlighted in the whitepaper. Manufacturers are developing internal governance programs for data and AI systems, with a focus on protecting data privacy and conducting thorough internal testing before deploying new programs. This is particularly true for heavily regulated industries such as automotive, pharmaceuticals, and aerospace, which already meet many safety benchmarks applicable to AI systems. The importance of rigorous AI testing and governance is especially pronounced in aerospace and automotive manufacturing, where safety, reliability, and compliance are paramount.
44% of professionals cite data privacy and cybersecurity as the top challenges associated with increased system connectivity in AI-driven environments. Additionally, manufacturers face a digital readiness gap, with only 21% considering themselves fully 'AI ready' due to outdated systems and data quality issues.
The report also notes that many manufacturers are working directly with government agencies to develop certifications for critical technologies. This collaboration aims to ensure safety standards are met without disrupting AI system deployment.
This focus on testing and governance demonstrates the manufacturing industry’s commitment to responsible AI development and deployment. It also highlights the need for flexible regulatory frameworks to keep pace with rapidly evolving AI technologies while ensuring safety and reliability.
How to Measure the Success of AI in the Manufacturing Industry?
The adoption of digital technologies such as virtual reality and augmented reality further enhances the ability to monitor and improve manufacturing operations. These tools provide immersive, real-time insights into production lines, helping teams visualize data and collaborate more effectively.
The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of AI adoption in manufacturing continues to rise, driven by tangible benefits such as cost reduction and improved efficiency. By analyzing historical data with AI, manufacturers can spot trends, refine their strategies, and allocate resources more effectively. This data-driven approach ensures that AI investments deliver measurable returns, supporting continuous improvement and long-term success in a competitive market.
Sustainability and AI
Predictive maintenance, enabled by AI, helps extend equipment lifespans and reduce maintenance costs, thereby reducing the need for new raw materials and lowering the overall carbon footprint. In supply chain management, AI-driven insights allow companies to streamline logistics, reduce transportation emissions, and make more sustainable sourcing decisions.
Moreover, AI supports the development of eco-friendly products by identifying opportunities to use recycled materials or design for recyclability. By integrating AI into their sustainability strategies, manufacturers not only improve operational efficiency and reduce costs but also demonstrate a commitment to environmental stewardship. Embracing AI for sustainability positions manufacturers to meet regulatory requirements, satisfy customer expectations, and contribute to a greener future.
Policy Recommendations for AI in Manufacturing
The NAM whitepaper describes the current state of AI in manufacturing and makes several key policy recommendations to support its continued growth and responsible development in the sector:
First, the report suggests that policymakers should review existing laws before enacting new ones. This approach would help avoid creating duplicative and burdensome requirements, recognizing that many existing regulations may already address AI-related concerns.
Second, NAM advocates for context-specific AI regulation. The whitepaper argues that new regulations should differentiate among the variety of AI use cases, considering risk, deployment context, and human oversight. This nuanced approach aligns with how manufacturers are already developing internal governance structures to manage varying risk levels across AI applications.
Third, the report emphasizes the need to right-size compliance burdens. While ensuring safety and reliability is crucial, overly burdensome compliance requirements could stifle innovation. The whitepaper suggests policymakers should be mindful of potential compliance burdens, particularly for smaller manufacturers.
Fourth, NAM stresses the importance of maintaining U.S. global leadership in AI development and policy. The report calls for leveraging industry standards and best practices to enhance regulatory certainty and ease compliance. It also emphasizes the need for globally aligned regulatory environments to avoid a patchwork of incompatible laws that could hinder U.S. competitiveness.
Fifth, the whitepaper recommends increased investment in R&D and workforce development. Recognizing the critical role of a skilled workforce in AI implementation, NAM calls for the support of career and technical education institutions that train the industry's workforce.
Lastly, the report advocates for federal privacy legislation to protect personal data. NAM supports efforts to craft a federal privacy law that would advance individuals' privacy, prevent a patchwork of state privacy laws, and provide legal clarity to support continued innovation and competitiveness.
These policy recommendations reflect the manufacturing industry's desire to play a significant role in shaping AI policy and regulations. They aim to ensure the regulatory environment supports innovation while addressing key concerns about safety, privacy, and responsible AI development.
Industrial Challenges of Implementing AI
While the NAM whitepaper presents an overwhelmingly positive view of AI in manufacturing, it also acknowledges several challenges. One key concern is the need for a balanced regulatory approach that fosters innovation while ensuring safety. As AI technologies evolve rapidly, creating regulations that are both effective and flexible enough to accommodate future developments will be crucial.
Cybersecurity is another significant challenge highlighted in the report. As manufacturing operations become increasingly connected and reliant on AI systems, the potential for cyber threats grows.
Future Outlook for AI in Manufacturing
Looking ahead, the future of AI in manufacturing includes the emergence of fully autonomous factories, where AI systems control every aspect of production with minimal human intervention.
The report suggests that manufacturers will continue to expand their use of AI across various operations.
As AI technologies become more sophisticated and accessible, we expect to see even more innovative applications emerge. With its dual role as both developer and deployer of AI technologies, the manufacturing sector is well-positioned to lead this innovation and shape the future of AI in the industry.
Neural networks will power self-organizing, adaptive manufacturing systems that continuously learn and optimize processes. Additionally, digital marketing will become an integral part of manufacturing's digital transformation, helping companies build accurate consumer profiles and improve service experiences through AI-driven insights.
Conclusion
The whitepaper offers a comprehensive and insightful look at AI's current state and future potential in manufacturing. It's clear that AI is not a passing trend, but already transforming the manufacturing industry in significant ways. As manufacturers continue to innovate and push the boundaries of what's possible with AI, we can expect to see even more exciting developments in the coming years.
Sources:
https://nam.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/NAM-AI-Whitepaper-2024-1.pdf
https://www.futurebridge.com/industry/perspectives-industrial-manufacturing/machine-vision-the-future-of-quality-control-in-manufacturing/
