
Top Trends Transforming Risk & Audit
Risk Trends
Nov 26, 2025

Magdalena Rucińska
Content Specialist
The era of the "checklist auditor" is fading. In its place, a new breed of strategic advisor is emerging—one powered by real-time data, predictive AI, and continuous monitoring. Yet, a critical gap remains: while Deloitte’s Internal Audit 4.0 framework reveals that 82% of audit functions report increased impact, only 14% believe they’ve truly realized their full potential.
Bridging this gap requires more than just new software; it demands a fundamental shift in mindset. At Parakeet Risk, we are tracking the main trends reshaping industrial risk management—from digital twins in manufacturing to AI that predicts risks before they materialize. Here is how innovation is transforming internal audit from a retrospective compliance function into a proactive engine of value.
Why Traditional Audits Fail in High-Stakes Manufacturing?
In high-stakes industries like manufacturing, the difference between a minor operational hiccup and a costly regulatory failure often comes down to the speed of insight. Traditional, sample-based audits are no longer sufficient in a world defined by complex global supply chains and rapid regulatory changes.
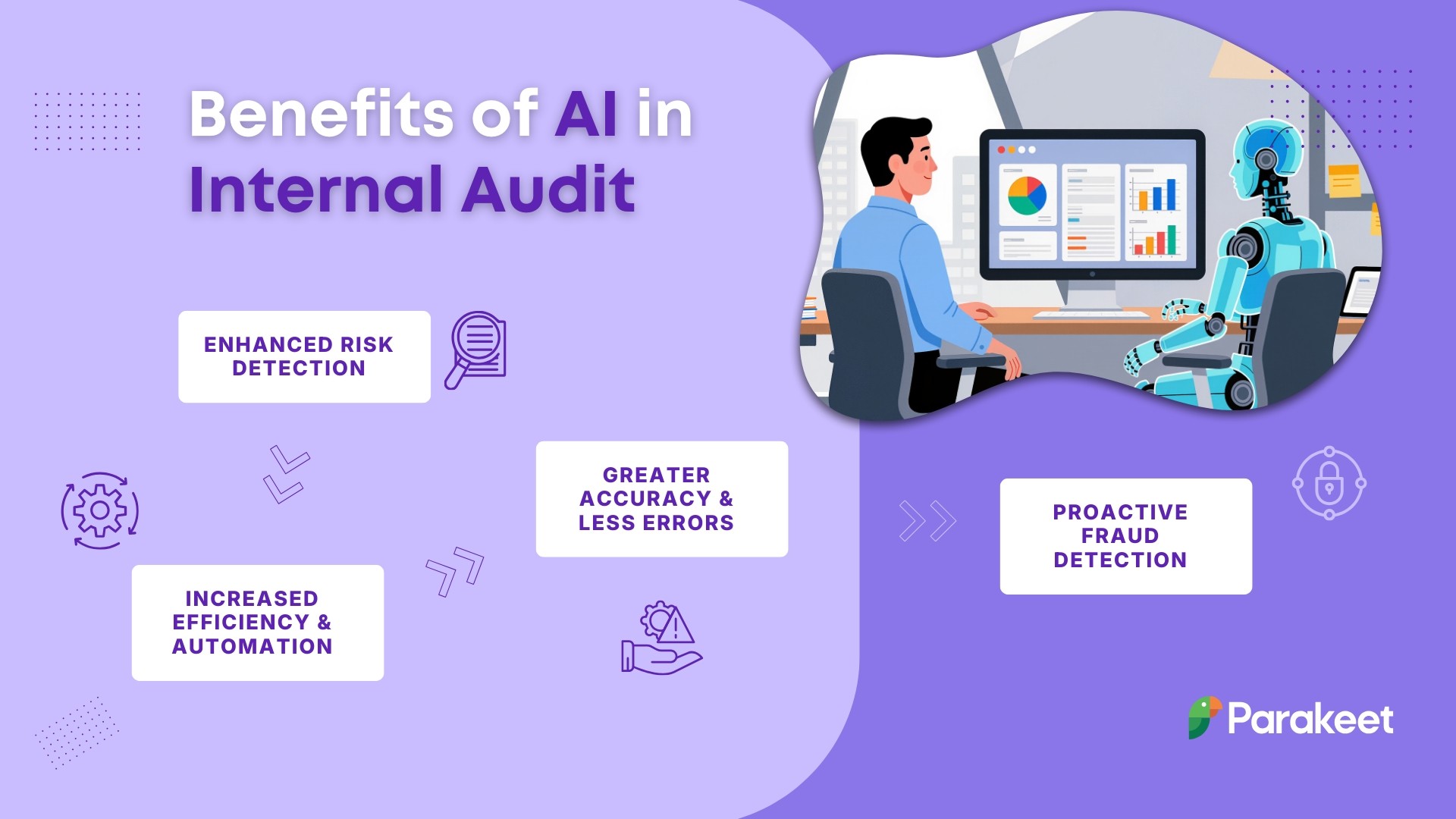
Revolutionizing Risk Assessments with AI in Internal Audit
AI is fundamentally transforming how internal auditors identify, assess, and mitigate risks. Traditional risk assessments relied on manual processes, spreadsheets, and subjective judgment—methods that were time-consuming and prone to bias. Today's intelligent risk assessment leverages AI to automate data collection and analysis, freeing auditors to focus on strategic decision-making.
Deloitte’s Internal Audit 4.0 framework reveals that while 82% of functions report increased impact, only 14% believe they’ve realized their full potential.
For example, AI-powered tools, like Parakeet Risk can analyze entire transaction populations to detect anomalies and potential risks that may go unnoticed in sample-based audits.
👉 You may find interesting: The Hidden Stress of Safety Audits
The power lies in AI's ability to analyze massive datasets and recognize patterns that humans might miss. Machine learning models can predict future risks by learning from historical data, particularly valuable for analyzing highly repetitive transactions common in manufacturing environments. AI-enhanced surveys go beyond checkbox responses, using natural language processing to analyze open-ended feedback and identify custom risk factors unique to each organization.
For manufacturing firms managing thousands of daily transactions across global supply chains, AI can automatically detect anomalies, flag emerging threats, and provide real-time risk insights that enable proactive intervention rather than reactive responses.
Advanced Data Analysis for Pattern Detection
AI transforms how auditors analyze both structured and unstructured data. Traditional audit approaches have long been valuable, but AI takes analysis several steps further. Machine learning algorithms now analyze audit exceptions themselves—identifying patterns in false positives to recommend parameter adjustments, thereby reducing wasted effort and audit fatigue.
AI can uncover anomalies within the exceptions that human auditors might miss.
Leveraging Blockchain and Predictive Analytics for Enhanced Internal Audit Insights
Blockchain technology is also being explored to provide tamper-proof audit trails, which increase transparency and trust in financial reporting. Additionally, auditors now use predictive analytics to anticipate emerging risks and support better decision-making within organizations. These innovations enable internal audit functions to deliver deeper insights and real-time risk management, positioning them as crucial partners in achieving organizational objectives in an increasingly complex regulatory environment.
Digital Twins for Audit and Risk Assessment
Digital twin technology—creating virtual replicas of physical assets, processes, or entire systems—is revolutionizing how internal auditors assess controls and simulate risks before they materialize in the real world. A digital twin maintained through continuous data exchange between the virtual model and its physical counterpart enables auditors to conduct thorough assessments without physical presence, increasing efficiency and reducing operational disruptions.
For manufacturing audit, digital twins enable auditors to simulate production line scenarios, stress-test controls under various conditions, and identify vulnerabilities before they occur. Rather than evaluating controls after a failure, auditors can test how controls would perform under different scenarios—equipment failures, supply chain disruptions, or cybersecurity incidents—and recommend improvements proactively.
Audit Automation
Automation addresses the challenge of third-party and supplier risk management, which has become increasingly complex for global manufacturers. Automated third-party risk management systems can reduce vendor onboarding time from 45 days to just 6 days while maintaining compliance standards, continuously monitoring vendor performance, financial health, and regulatory compliance across thousands of suppliers.
Continuous Control Monitoring: From Periodic to Perpetual
The vision of continuous audit has existed for over a decade, but practical implementation has remained elusive due to challenges in data access and analytics program development. Natural language processing now allows auditors to describe their analytical needs in plain language—"show me aging invoices between 30 and 60 days"—and have the AI automatically build the necessary scripts. This dramatically reduces the technical barrier to implementing continuous monitoring and accelerates the journey to mature, automated audit programs.
The shift from periodic audits to continuous control monitoring (CCM) represents a fundamental evolution in audit methodology. CCM dashboards built on existing internal control systems provide real-time notifications of anomalies. It allows issues to be addressed immediately rather than discovered months later during scheduled audits. This approach is particularly critical in manufacturing, where production line disruptions, quality control failures, or safety violations can have immediate and costly consequences.
Automation reduces costs by streamlining processes and minimizing manual interventions. Automated monitoring and testing improve operational efficiency. Organizations implementing continuous monitoring report significant improvements in audit coverage, with 59% now testing all controls instead of only the most critical ones—a 26% year-over-year increase.
The impact on communication and collaboration is equally significant. AI democratizes data analytics, allowing stakeholders across the organization to query data in everyday language and contribute actively to risk management. By sharing data-driven insights with departments, internal audit transforms from a policing function into a trusted value partner that illuminates previously hidden risks and opportunities.
Cybersecurity and Technology Integration
As manufacturing becomes increasingly digitized through IoT sensors, cloud-based systems, and interconnected supply chains, cybersecurity risks multiply. The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) sets new standards for operational resilience. Internal auditors must assess IT governance resilience, review third-party risks in interconnected ecosystems, and audit the ethical use of AI and automation within business processes.
The challenge is compounded by a severe skills shortage—
39% of organizations identify skills gaps as a major barrier to resilience, with only 14% having the necessary talent to achieve cybersecurity goals.
Manufacturing firms can address this through strategic blending of internal teams with external consultants who conduct gap analyses, map controls to risks, and provide actionable recommendations before external audits begin.
👉 Read more about The Supply Chain Cybersecurity
Navigating Regulatory Complexity: The Path Forward
The regulatory landscape for manufacturers has become a complex patchwork of global, federal, and state requirements. While some jurisdictions move toward stricter environmental policies, others adopt more relaxed standards—creating compliance challenges for organizations operating across multiple regions. Internal audit's role is evolving from reactive compliance checking to proactive risk management that leverages technology to manage workflows and align organizations with evolving standards like ISO 45001 and OSHA.
The cost of non-compliance continues to rise, making proactive compliance audits focusing on high-risk areas like workplace safety, emissions reporting, and product labeling essential for preventing costly fines. AI and automation enable auditors to stay ahead of regulatory changes, automatically updating risk assessments as new requirements emerge.
Sources:
World Economic Forum's "Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025"
https://www.weforum.org/stories/2025/06/cybersecurity-jobs-rise-us-industries-navigate-economic-uncertainty/
https://hyperproof.io/resource/the-future-of-auditing-2025
https://www.pwc.com/mt/en/services/pwc-digital-services/cyber-security-and-privacy/cyber-security-services/dora.html

